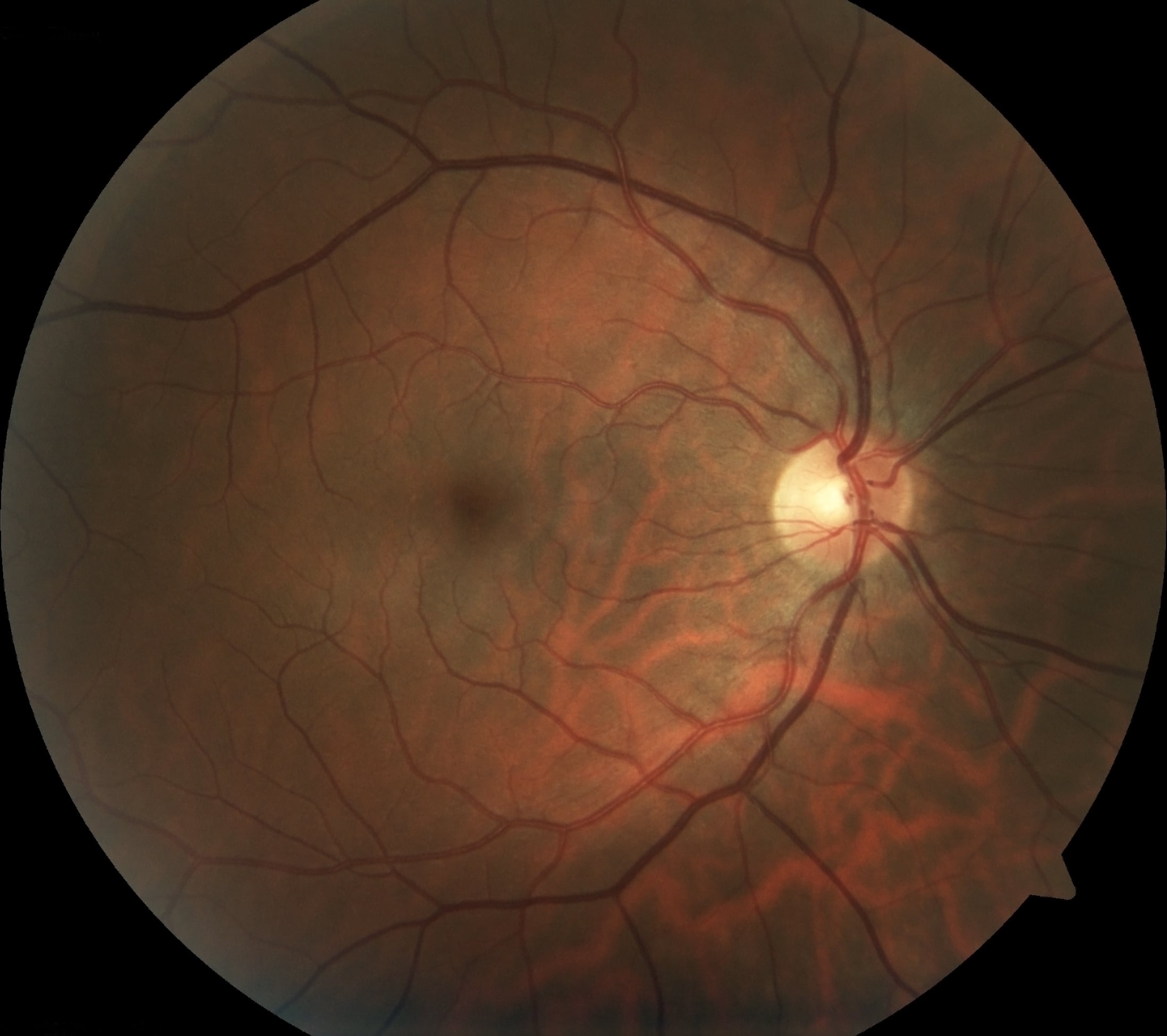
What we can see with retinal and optical coherence tomography imaging
Having good vision is something many people take for granted, but those who struggle with vision impairment in some way or another appreciate the importance of having a competent and trustworthy optometrist. Advances in technology such as retinal imaging not only improve the way optometrists diagnose their patients, but also make it easier to diagnose, treat and even prevent conditions from developing.
What is Retinal Imaging?
Retinal imaging is a relatively recent development. A digital image is taken by a highly sophisticated camera that captures an image of the patient’s retina, including the blood vessels and optic nerves located at the back of the eye. The images are immediately sent to a computer viewing system, where the optometrist can access the images and discuss the results with their patient. Dilation is not required for retinal imaging to be effective, but may be recommended by your doctor.
These scans are saved into a digital archive and stored for any future visits. This makes it easier for your optometrist to retrieve your personal data and facilitates care and treatment. These photos can be compared and contrasted with later retinal images.
Optical Coherence Technology
Optical Coherence Technology (OCT) is another technique for taking retinal images. OCT uses an invisible spectrum of light on a wavelength approaching infrared. This technique of imaging allows three-dimensional scans of the retina to be captured at incredibly high resolutions.
These scans, like retinal imaging, are stored into a computer database for withdrawal and comparison at any time. These images are incredibly useful for detecting and diagnosing a variety of optical infections and diseases.
Why Optometrists Employ Digital Imaging Technology
There are advantages to both digital retinal imaging and OCT. For example, a retinal image is able to capture an image of the entire eyeball, or at least a large portion of it. This is far more effective and time-efficient that traditional methods, which require optometrists to analyze small samples of the retina at a time.
Retinal imaging also provides a more detailed view into your retina than conventional methods. You could compare this to looking at a leaf with a magnifying glass. Certain details become apparent which were simply invisible earlier. This makes it easier for your optometrist to notice any possible issues with your retina.
The images taken by OCT are quite different than those taken by digital retinal imaging, but they are no less effective, and are used to detect different symptoms. What an OCT scan allows an optometrist to do is to observe the different layers of the retina. It also enables them to discern the thickness of the retina. Basically, OCT images record the structure of the eye, something a traditional visual scan cannot due.
Both of these scans are most effective when used in conjunction with traditional visual methods. This leads to the best and most accurate results.
How Digital Imaging Aids Diagnosis
These imaging tests are useful for detecting a variety of optical conditions. These conditions include macular degeneration, glaucoma, retinal detachment, and diabetic retinopathy. In some of these cases, early diagnosis can prevent some of the damage done to the eye.
Macular Degeneration
While there are several types of macular degeneration, the process is often the result of aging. The macula is a small part of the retina that nevertheless fulfills an important role, as it is responsible for the ability to see details clearly. Those suffering from macular degeneration may experience various symptoms, such as blurriness or an inability to see details clearly. Your peripheral vision is usually unaffected.
Glaucoma
Glaucoma is a disease that affects the optic nerves. It is associated with elevated pressure inside of the eye. As this pressure builds, it can permanently damage the optic nerves, resulted in impaired vision or even blindness. An OCT scan can detect if the eye is in the early stages of glaucoma, and preventative measures and treatments can minimize the effects.
Retinal Detachment
Retinal detachment is just like it sounds. For one reason or another, the retina begins to pull itself away from the wall of the eye. If this is not caught in time and treated, it can lead to permanent blindness. It is sometimes caused by small tears in the retina that pull away from the inside lining of the eyeball.
Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetic Retinopathy is a common side effect of diabetes. It is caused as a result of changes in the blood vessels flowing to the retina. These changes can include blood leaks, swollen vessels or even abnormal growths of new blood vessels to the retina.
Good vision should never be taken for granted. Optical diseases can strike at any time and can reduce perfect 20/20 vision to blindness. Take steps to protect your vision. Contact us today to setup an optical exam. Your eyesight is too precious to take chances.